리액트 상태관리 - Flux & useReducer
Flux 아키텍쳐
Redux : Flux 아키텍쳐 기반 라이브러리
-
unidirection data flow
-
action 을 전달
-
store에서 데이터 변경 관리
-
view는 store를 구독하는 방식
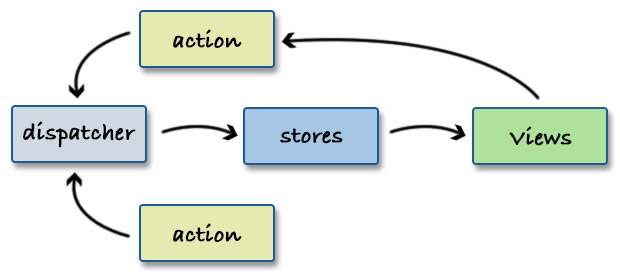

image: https://redux.js.org/assets/images/ReduxDataFlowDiagram-49fa8c3968371d9ef6f2a1486bd40a26.gif
//view에서
dispatch({
type: 'deposit',
payload: 10
})
//reducer에서
switch (action.type) {
case "deposit":
return {
action.payload
}
....
.....
useReducer Hooks API - flux 아키텍쳐를 따름
useReducer API
복잡한 상태관리에서 useState보다 유리하다.
구체적인 상태변경을 감추고, reducer에 맡길 수 있다.
또한 콜백(setState 등)을 계속 하위component 에 전달해줘야 하는 불편함을 줄일 수 있다. 대신 dispatch라는 매개체 역할의 함수를 전달해준다.
참고 : https://react.dev/reference/react/useReducer
const initialState = {count: 0};
function reducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'increment':
return {count: state.count + 1};
case 'decrement':
return {count: state.count - 1};
default:
throw new Error();
}
}
function Counter() {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState);
return (
<>
Count: {state.count}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({type: 'decrement'})}>-</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({type: 'increment'})}>+</button>
</>
);
}
useReducer + Context API
-
Hooks API에서도 Flux architecture 를 따르며 개발 가능.
-
view 에서 상태변경 로직도 분리.
-
“그렇다면 Redux를 어느정도 대체가능?”
-
Context API 조합으로 같이 사용하면 어떨까?
const postReducer = (posts, { type, payload }) => {
switch (type) {
case 'SET_INITIAL':
return [...payload];
case 'ADD_POST':
return [...posts, { title: payload, id: posts.length + 1, picked: false }];
case 'TOGGLE_PICKED':
return posts.map(post =>
post.id === payload ? { ...post, picked: !post.picked } : post
);
default:
return posts;
}
};
export const PostsContext = React.createContext();
const App = () => {
const [posts, dispatch] = React.useReducer(postReducer, []);
const addItemHandler = () => {
const newTitle = prompt("Enter new post title");
if (newTitle) {
dispatch({ type: 'ADD_POST', payload: newTitle });
}
};
return (
<PostsContext.Provider value={{ posts, dispatch }}>
<PickedItems posts={posts} />
<button onClick={addItemHandler}>ADD</button>
<Items posts={posts} />
</PostsContext.Provider>
);
};